Arthropod/Vector
Bacteria
Chemicals
Fungus /Mold
/ Yeast Metals Parasites Virus Other Arthropod/Vector
Bacteria
Chemicals
Fungus /Mold
/ Yeast Metals Parasites Virus Other
|
Hepatitis A-E
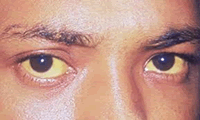
It has been noted that itchy skin has been an indication as a possible symptom of all hepatitis virus types. Use caution with personal-care items such as razors, toothbrushes, and manicure or pedicure equipment as it can be contaminated with blood. Tattooing is associated with two to three times higher risk of contracting hepatitis B & C viruses. Hepatitis B is caused by the virus HBV. About a third of the world population have been infected at one point in their lives, including 350 million who are chronic carriers. It is spread by contact with an infected person's blood, semen, or other bodily fluid. It is considered a sexually transmitted disease (STD). You can get hepatitis B by:
Acute hepatitis B causes the liver to swell and inflame, also causing vomiting and jaundice. Chronic hepatitis B may eventually cause cirrhosis and liver cancer. Hepatitis C is caused by the virus HCV. An estimated 130–170 million people worldwide are infected with hepatitis C. It is spread the same way as hepatitis B, through contact with an infected person's blood, semen, or body fluid (see above). Symptoms are generally mild and vague, including a decreased appetite, fatigue, nausea, muscle or joint pains, and weight loss. Most cases of acute infection are not associated with jaundice. The infection resolves spontaneously in 10-50% of cases, occurring more frequently in individuals who are young and female. Like hepatitis B, hepatitis C causes swelling of the liver and can cause liver damage that can lead to cancer. Most people who have hepatitis C develop a chronic infection that slowly (over decades) leads to scarring of the liver, called cirrhosis. Hepatitis D is caused by the virus HDV. You can only get hepatitis D if you are already infected with hepatitis B. It is spread through contact with infected blood, dirty needles that have HDV on them and unprotected sex (not using a condom) with a person infected with HDV. Hepatitis D causes swelling of the liver and results in more severe complications compared to infection with HBV alone. These complications include a greater likelihood of experiencing liver failure in acute infections and a rapid progression to liver cirrhosis, with an increased chance of developing liver cancer in chronic infections. Hepatitis E is caused by the virus HEV. HEV has a fecal-oral transmission route. You get hepatitis E by drinking water infected with the virus or contamination with infected feces. This type of hepatitis doesn't often occur in the U.S. It causes swelling of the liver, but no long-term damage. It can also be spread through oral-anal contact. |
|