|
|
Sporothrix
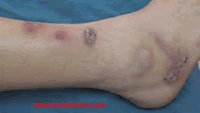 |
Sporotrichosis is a subacute or chronic infection caused by the soil fungus Sporothrix. It is often referred to as "rose handler's disease". Infection with the dimorphic soil fungus is usually acquired through skin penetration due to injury. A person can be otherwise healthy, but if this fungus enters the wound, it can cause severe infection.
The most common extracutaneous infection sites are in the bones, joints, tendon sheaths, and bursae. Hematogenous dissemination (originated from the blood), particularly in immunocompromised hosts, results in widely disseminated cutaneous and visceral infection, including meningitis.
A rare form of sporotrichosis appears to result from inhalation of the organism. This form is characterized by a chronic cavitary pneumonia that is clinically and radiographically indistinguishable from tuberculosis and histoplasmosis. This form of sporotrichosis is most common in individuals with severe underlying chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Sporotrichal infection of the larynx and paranasal sinuses has also been described.
|
|
|
 Arthropod/Vector
Bacteria
Chemicals
Fungus /Mold
/ Yeast Metals Parasites Virus Other
Arthropod/Vector
Bacteria
Chemicals
Fungus /Mold
/ Yeast Metals Parasites Virus Other